The FB VIS is a Polish semi-automatic pistol developed during the 1930s. Except for the caliber, it is an exact clone of the legendary M1911. The original M1911, designed by John Browning, was chambered in .45 caliber, while the VIS is chambered in 9x19mm.
History
The VIS name was derived from the names of its designers, Wilniewczyc and Skrzypinski. The original name was WIS, but it was changed to VIS, likely because VIS means “force” in Latin with the wz. abbreviation for wzór (“model”).
The development of the VIS began in 1930 at a Fabryka Broni (arms factory) in Radom city. The first prototype was completed in 1931, and the Polish Army tested it over four years. In 1935, the VIS was finally approved for use and was designated as the VIS wz.35. It became the standard-issue handgun for the Polish Army. Due to the markings on the slide, many people mistakenly refer to it as the “Radom.”

In 1939, when German forces captured the factory that produced this pistol, production continued for the German military. The pistol was known as the P-35 and was issued to the German navy, paratroopers, police, and SS units. However, Polish workers at the factory began smuggling parts of the pistol out to arm resistance fighters. When the Germans discovered this, they executed several plant workers. In response, the Germans moved the machinery to Austria and began making barrels to prevent sabotage. The pistols were then assembled using original Polish-made parts.
Many different versions of the VIS pistol have been manufactured since its introduction. Many experts consider the VIS to be one of the best WWII-era pistols. In 1992, production of the VIS was restarted, and a limited number of exact copies were produced for civilian customers and collectors.
Design
The VIS is a 9mm clone of the M1911 pistol developed by John Browning. At the time, the patents for the M1911 were expiring, so the VIS was developed as a similar, but slightly different, design. The VIS also has some features of the Hi-Power pistol, which Browning also developed. However, both the VIS and the Hi-Power were developed around the same time and adopted in 1935.
The VIS is a short-recoil-operated weapon. The barrel locking system is similar to that of the Browning Hi-Power. The VIS has a single-action trigger and no manual safeties. There is an M1911-style grip safety, but the lever on the frame is not a safety. Instead, it is a slide-retaining latch that aids in disassembling the pistol. There is also a decocker switch on the slide.
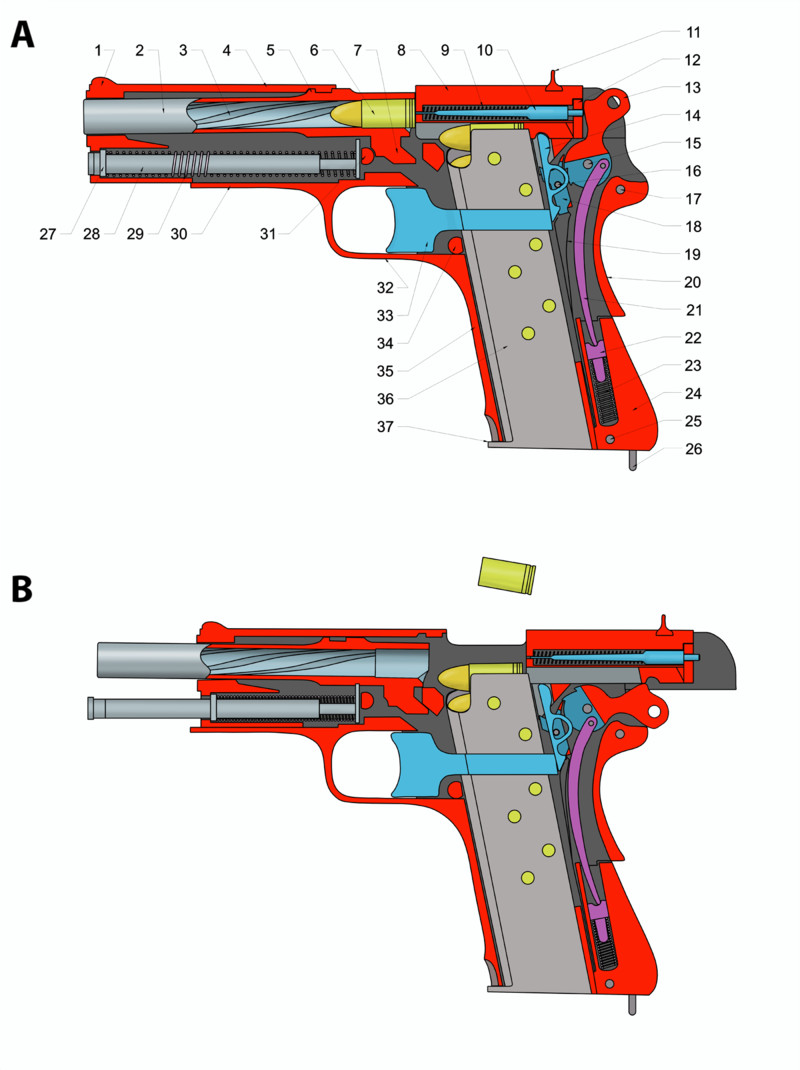
This pistol is well-made and robust, but the quality was reduced when the Germans took over the factory in 1939. As production progressed, the Germans simplified its manufacturing process. The VIS is fed from single-stack 8-round capacity magazines. It has simple iron sights, and the effective range of fire is about 50 meters. The VIS is more accurate than the contemporary Soviet TT pistol but has less penetration power. Polish VIS pistols produced between 1935 and 1939 had a grip mount for shoulder stock.

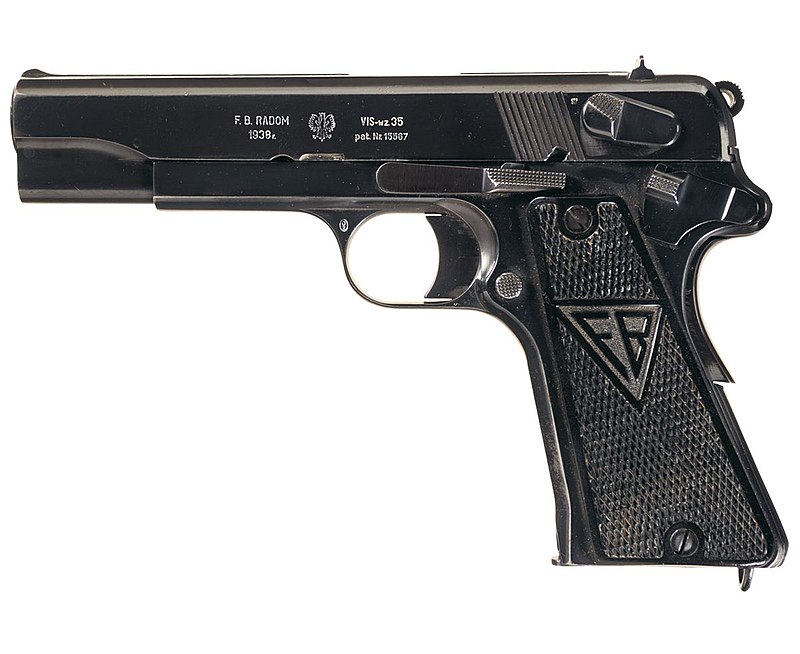
Variants
In addition to the 9mm version, a small series of VIS pistols chambered in .45 ACP, with a 7-round magazine, but they were not produced in large numbers. Only a few were likely made for an Argentinian competition, but no examples of these pistols with wooden shoulder stocks have survived. A .22 LR variant also existed, but no details are known, and it was not produced in significant numbers.
Users
- Poland – Standard issue sidearm of the Polish Army from 1935 to 1939, later they were used by Polish Underground and the post-war Polish independence and anti-communist underground.
- Nazi Germany – Factory captured in World War II, used primarily by the Fallschirmjäger.
- Italian Partisans – Captured from German soldiers.
- Free France – Captured by German soldiers and used by resistance fighters.
Technical specifications
| Country of origin: | Poland |
| Manufacturer: | Fabryka Broni Radom |
| Entered service: | 1935 |
| Caliber: | 9×19 mm Parabellum |
| Weight (empty): | 1 025 g |
| Length: | 205 mm |
| Barrel length: | 115 mm |
| Muzzle velocity: | – |
| Magazine capacity: | 8 rounds |
| Sighting range: | 50 m |
| Range of effective fire: | 50 m |



Not particularly accurate. Makes several statements (eg 1911 clone,.45 acp version, post war production) that need proof
Exact clone? 🤗