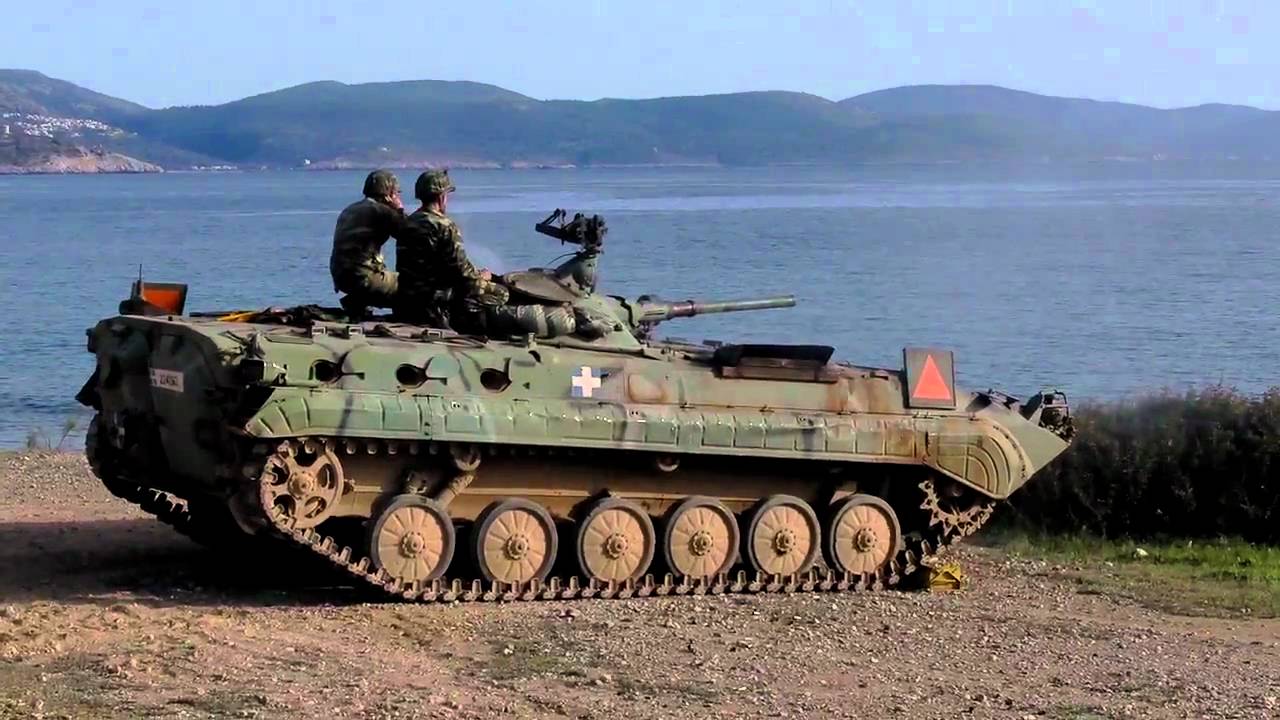
The BMP-1 is the first mass-produced infantry fighting vehicle (IFV) of the SSSR. It is tracked vehicle which has full amphibious capability. One of its most important features is a front-engined chassis developed especially for it, a welded steel hull with a sharp, sloping front with a conspicuously ridged surface, and a centrally located, flat, truncated cone turret with a troop compartment at the rear.
Introduction
BMP-1 is an Infantry Fighting Vehicle (IFV) developed in the early 1960s to replace BTR-50P series tracked APCs and was first seen in public in 1967. It was replaced in production by BMP-2 ICV, which, although similar in appearance, has a slightly different layout and new turret and weapon system. The latter followed BMP-3.
Design
In the BMP-1, the driver sits front left with the vehicle commander to the rear, and the engine compartment is to the right of the driver with a one-man turret center and troop compartment rear. Turret power traverses through 360 degrees, and a 73mm gun elevates from -4 degrees to +33 degrees and fires HEAT or HE-FRAG rounds. 7.62mm machine gun is mounted coaxial to the right of the 73m gun, and mounted over the gun is the launcher for AT-3 Sagger wire-guided ATGW, which has a maximum range of 3,000m.
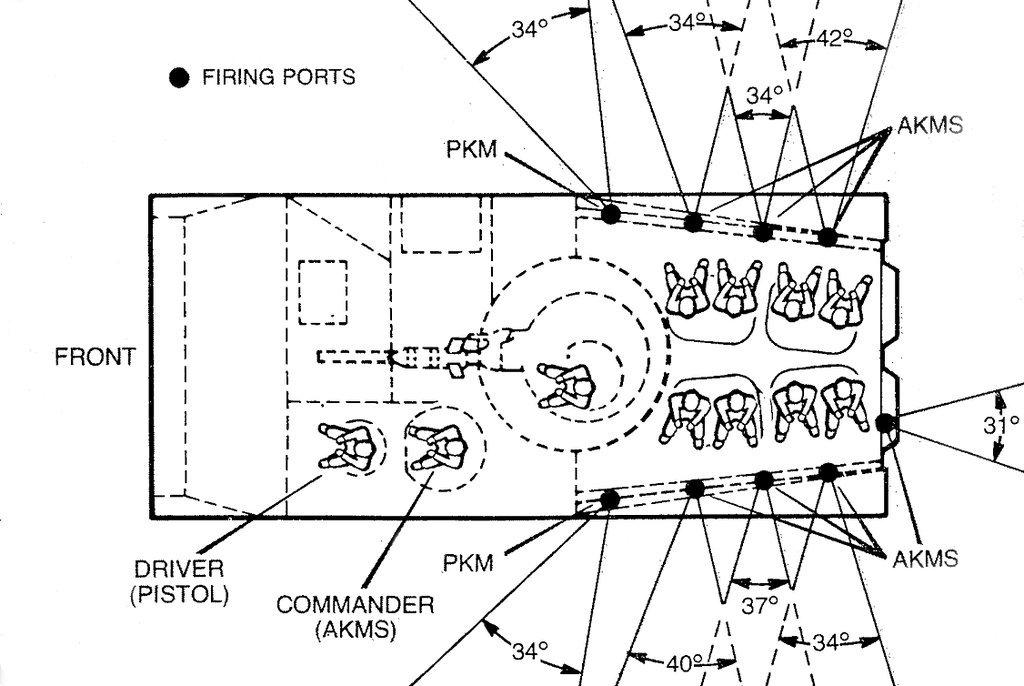
The troop compartment is at the rear with eight infantry seated, four on each side, back to back. On each side of the troop compartment are four firing ports with a periscope above and in each of the two rear doors is a further firing port and periscope.
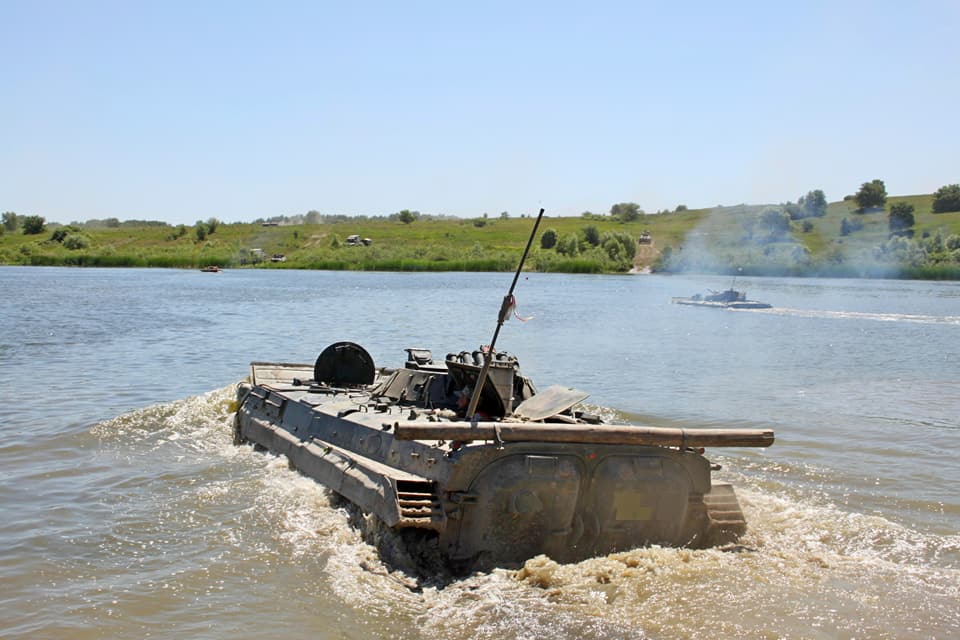
BMP-1 is fully amphibious, propelled by its tracks. Before entering the water, a trim vane is erected in front of the vehicle, and bilge pumps are switched on. As BMP-1 was produced for some 20 years, there are minor detailed differences between production models.
Key recognition-features
Pointed nose with almost horizontal ribbed glacis plate, driver front left, engine compartment louvers in the roof to the right, turret slightly to the rear of the vehicle, troop compartment rear with four roof hatches, two on each side. Vertical hull rear with two bulged doors opening rear. Similar in appearance to BMP-2 but with a different turret with a long-barreled 30mm cannon and a wider hull
A circular turret with well-sloped sides has a 73mm gun with a launcher above for Sagger ATGW (not always installed in peacetime) single gunner’s hatch on the left side of the roof. Four firing ports on each side of the hull and three on each rear door
Suspension on each side has six road wheels, a drive sprocket at the front, an idler rear, and three track-return rollers—the upper part of the track is covered by skirts.

Variants
- BMP-1F, reconnaissance model used by Hungary
- BMP-1K, BMP-1 commander’s model
- BMP-1K3, BMP-1 commander’s model
- BMP-1P, BMP-1 with no Sagger, and roof-mounted AT-4 ATGW fitted
- BMP-1PK, BMP-1P commander’s model
- BRM-1K, BRM-1 basic reconnaissance – armored cavalry
- BREM-1 and BREM-4, recovery vehicles
- BMP-1KShM, an unarmed command version of BMP-1
- BWP, the Polish version of BMP-1
- Czech BMP-1, many variants including OT-90 (BMP-1 with the turret of OT-64C(1))
- Egyptian BMP-1 has a new French diesel engine
- BMP-1 can be fitted with mine-clearing equipment
- BMP-1 has been equipped with a 30mm grenade launcher
- BRM and BRM-1 reconnaissance vehicles, new two-man turret
- PRP-3 Radar, two-man turret in radar on the roof
- IRM, amphibious reconnaissance vehicle
- BMP-POO, Mobile training Centre, no turret, raised roof, Iraqi versions include ambulance and basic vehicle with applique armor
- BMP-1G, for export, no Sagger, roof-mounted Spandrel ATGW plus 30mm grenade launcher

Status
The vehicle was in service with Afghanistan, Algeria, Angola, Bulgaria, Russia, Cuba, Egypt, Ethiopia, Finland, Greece, Hungary, India, Iran, Iraq, North Korea, Libya, Mongolia, Poland, Romania, Sri Lanka, Sweden, Syria, Yemen, and former Yugoslavia.
Today, a dozen countries are still using it, but the major countries with more than 1,000 units in active service are Russia, India, Poland, and the People’s Republic of China.
Conflicts
The BMP-1 was first tested in combat in the 1973 Yom Kippur War, where Egyptian and Syrian forces used it. Based on lessons learned from this conflict and early experiences in the Soviet-Afghan War, a version with improved fighting qualities was developed, the BMP-2 and BMP-3, that followed later.
Syrian Civil War
It was used widely in the Syrian civil war, first by Syrian government forces and later with almost all factions owning some of the vehicles. It was also used as VBIED (vehicle-borne improvised explosive devices) in suicide attacks. The vehicle’s advantages in this role are the large capacity of explosives it can carry, the off-road capability afforded by tracks, and the armor that both protects the driver from fire and amplifies the effect of the explosion.
Ukraine War
During Ukraine War, Ukrainian Armed Forces had dozens of those IFVs at their disposal. At the beginning of April, Germany announced that it would send a total of 56 those IFVs to Ukraine to support its defense against the Russian invasion. Most of them had previously been in service in Eastern Germany.
Manufacturer
Former Czechoslovak and Russian state’s arsenals. China has its version of this IFV designated as WZ 501.
Technical specifications
| Country of origin: | SSSR |
| Manufacturer: | Former SSSR arsenals |
| Crew: | 3+8 |
| Armament: | 1 x 73mm, 1 x 7.62mm MG (coaxial), 1 x Sagger ATGW launcher |
| Ammunition: | 40 x 73mm, 2000 x 7.62mm, 1+4 Sagger ATGW |
| Length: | 6.74m |
| Width: | 2.94m |
| Height over searchlight: | 2.15m |
| Ground clearance: | 4.75m |
| Height without AA MG: | 0.39m |
| Weight, combat: | 13,500kg |
| Weight, empty: | 12,500kg |
| Power-to-weight ratio: | 22.22hp/tonne |
| Ground pressure: | 0.6kg/cm2 |
| Engine: | Type UTD-20 6-cylinder in-line water-cooled diesel developing 300hp at 2,000rpm |
| Maximum road speed: | 65km/hr |
| Maximum water speed: | 7km/hr |
| Maximum road range: | 600km |
| Fuel capacity: | 460 lit |
| Fording: | Amphibious |
| Vertical obstacle: | 0.8m |
| Trench: | 2.2m |
| Gradient: | 60% |
| Side slope: | 30% |
| Armor: | 33mm (maximum) |
| Armor type: | Steel |
| NBC system: | Yes |
| Night vision equipment: | Yes (infra-red for commander, gunner, and driver) |





